Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (39): 6233-6239.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.39.001
Rebuilding injured vertebrae by different kinds of bone graft materials to treat thoracoiumbar burst fractures: an imaging verification of bone healing
Shi Xiao-lin, Liu Qing-ge, Zhang Hao, Tian Yue, Yang Yong-ming, Yuan Wei-dong
- Department of Orthopaedics, the Second Hospital of Baoding, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2014-09-17Published:2014-09-17 -
Contact:Tian Yue, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, the Second Hospital of Baoding, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Shi Xiao-lin, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopaedics, the Second Hospital of Baoding, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Xiao-lin, Liu Qing-ge, Zhang Hao, Tian Yue, Yang Yong-ming, Yuan Wei-dong. Rebuilding injured vertebrae by different kinds of bone graft materials to treat thoracoiumbar burst fractures: an imaging verification of bone healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(39): 6233-6239.
share this article
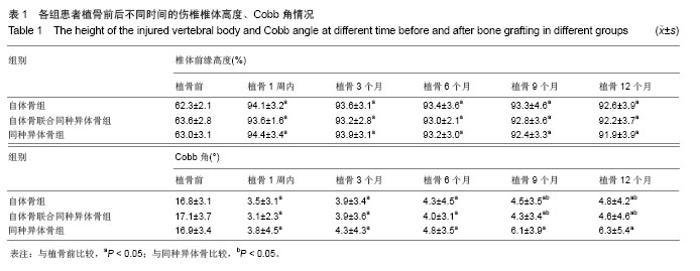
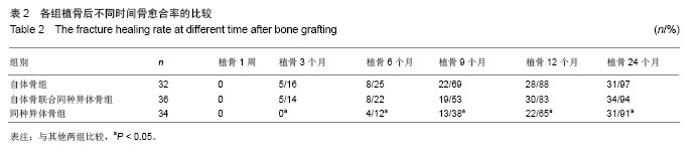
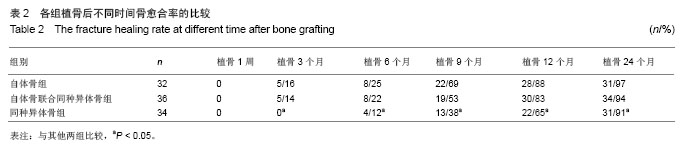
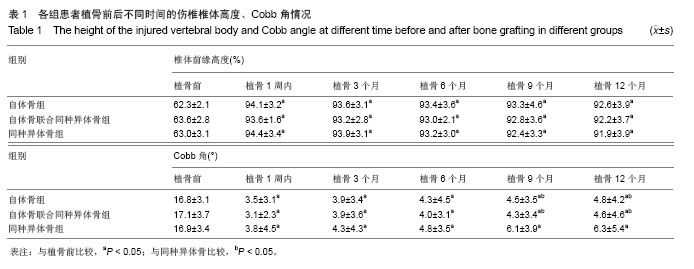
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理分析,纳入的102例胸腰椎爆裂骨折患者全部进入结果分析。 2.2 随访情况 102例患者均获得24-36个月随访,平均随访27.1个月。 2.3 手术操作并发症 所有患者伤椎均完成单侧置钉、植骨,未因伤椎单侧置钉、植骨操作引起脊髓神经损伤或加重,手术部位无感染。 2.4 影像学结果比较 3组植骨后各时间点伤椎椎体前缘高度百分比及Cobb角与植骨前比较均明显恢复(P < 0.05)。植骨9个月以后,3组椎体前缘高度及Cobb角比植骨后6个月内均有所增加,但3组间植骨后各时间点椎体前缘高度百分比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);同种异体骨组植骨9个月后Cobb角较植骨后1周增加明显(P < 0.05),但自体骨组、自体骨联合同种异体骨组各时间点Cobb角比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。自体骨组、自体骨联合同种异体骨组植骨后各时间点的骨愈合率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),同种异体骨组和自体骨组、自体骨联合同种异体骨组间各时间点的骨愈合率比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。"
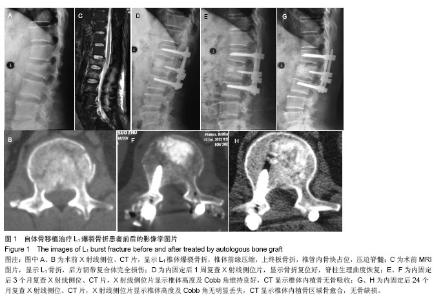
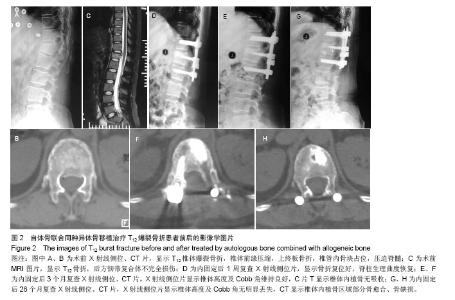
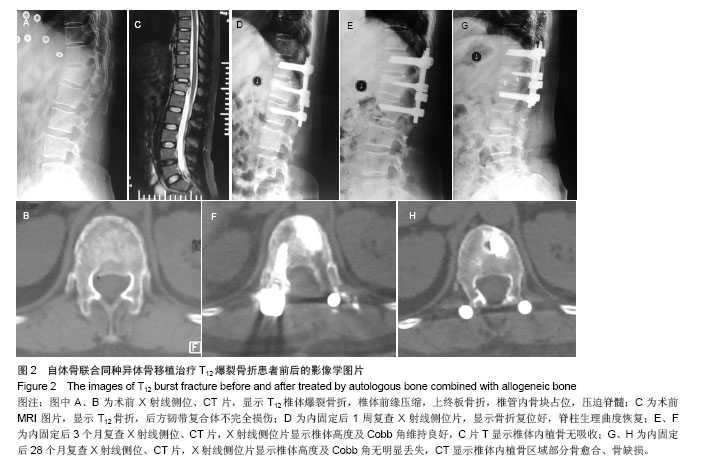
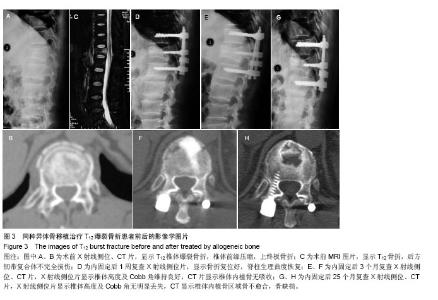
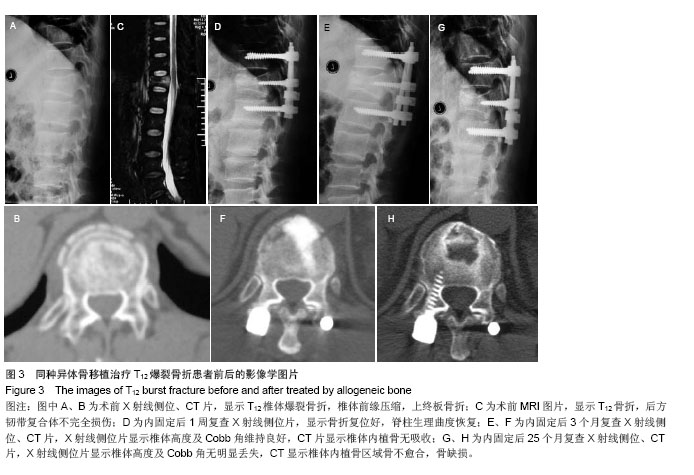
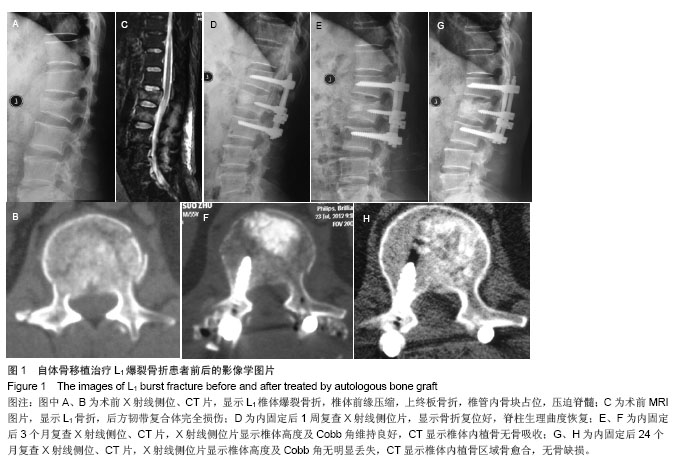
2.5 终末随访CT椎体内骨缺损情况 同种异体骨组的骨缺损面积(8.1±4.2)%与自体骨组(3.1±2.2)%、自体骨联合同种异体骨组(4.2±3.7)%比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.6 不良反应 自体骨组和自体骨混合同种异体骨组切口均Ⅰ期愈合,无排斥反应等并发症;同种异体骨组有3例患者出现伤口红肿渗液,行细菌培养无细菌生长,经局部换药处理后愈合;无使用同种异体骨出现感染肝炎或艾滋病者。 2.7 典型病例 病例1:55岁男性患者,因高空坠落伤致L1爆裂骨折合并不完全性脊髓损伤,骨折累及L1椎体,Denis B型骨折,术前载荷评分7分。患者入院后7 d全身病情稳定,在全麻麻醉下行腰后路T12-L2椎弓根内固定椎管减压、伤椎单侧置钉、对侧经椎弓根椎体内植入自体骨,术后随访24个月,术后复查影像学提示椎体骨折复位满意,脊髓损伤恢复,终末随访CT显示椎体内植骨区域骨愈合(图1)。"
| [1]Alanay A,Acaroglu E,Yazici M,et al.Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(2):213-217. [2]李利,史亚民,候树勋,等.经椎弓根椎体内植骨与后外侧植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的影像学研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2011,49(2): 140-144. [3]赵栋,邱贵兴,仉建国.腰椎融合技术及其临床研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(4):298-300. [4]Cragg A,Carla A,Castaneda F,et al.New percutaneous access method for minimally invasive anterior lumbosacral surgery.J Spinal Disord Tech.2004;17(1):21-28. [5]Jensen SS,Terheyden H,Bone augmentation procedures in localized defects in the alveolar ridge:clinical results with different bone grafts and bone-substitute materials.lin J Oral Maxillofac lmplants.2009;24(Suppl):218-236. [6]Khojasteh A,Behnia H,Shayesteh YS,et al.Localized bone augmentation with cortical bone blocks tented over different particulate bone substitutes:aretrospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2012;27(6):1481-1493. [7]Bose S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A.Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds.Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10): 546-554. [8]Zimmermann G,Moghaddam A.Allograft bone matrix versus synthetic bone graft substitutes.Injury.2011;42(2):16-21. [9]Rush SM.Bone graft substitutes:osteobiologics.Clin Podiatr Med Surg.2005;22(4):619-630,viii. [10]Friedlaender GE.Immune responses to osteochondral allografts.Current knowledge and future direction.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;174(4):58-68. [11]Muscolo DL,Caletti E,Schajowecz F,et al.Tissue-typing in huma massive allografts of frozen bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1987;69(4):583-595. [12]Guo S,Feng W,Jia Y.Lyophilized small-segment allogeneic bone in repairing bone defect due to benign bone tumor and tumor-like lesions after resection and curettage.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2007;21(8):789-792. [13]Buecker PJ,Gebhardt MC.Are fibula strut allografts a reliable alternative for periarticular reconstruction after curettage for bone tumors?.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007;461(8):170-174 [14]Smrke D,Gubina B,Domanovic D, et al.Allogeneic platelet gel with autologous cancellous bone graft for the treatment of a large bone defect.Eur Surg Res.2007;39(3):170-174. [15]施建党,王自立,王沛,等.同种异体骨与自体骨在颈椎结核植骨融合中的应用比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(11): 1290-1293. [16]史晓林,杨永明,张昊,等.经伤椎椎弓根植骨结合椎弓根螺钉治疗胸腰椎骨折远期疗效[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(4):265-266. [17]Daniaux H.Transpedicular repositioning and spongioplasty in fracture of the vertebral bodies of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine.Unfallchirurg.1986;89(5):197-213. [18]周飞,魏丽红.同种异体骨结合自体骨经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(1):12-14. [19]张少华,牛海涛,张斌,等.经椎弓根椎体内植入自体骨、同种异体骨、重组蛋白异体骨骨碎块等材料治疗胸腰段爆裂骨折56例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19):3677-3680. [20]Ito Z,Matsuyama Y,Sakai Y,et al.Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(21): E1101-1105. [21]Myeroff C,Archdeacon M.Autogenous bone graft:donor sites and techniques.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2011;93(23): 2227-2236. [22]袁振超,陈远明,陈锋,等.腰椎滑脱症椎间植骨融合中3种植骨材料的远期效果对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2013, 17(16):3033-3040. [23]Tomford WW.Bone allografts:past,present and future.Cell Tissue Bank.2000;1(2):105-109. [24]山富彦.不同植骨材料联合钉棒系统在胸腰椎结核植骨融合术的应用和比较[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(14):2416-2418. [25]丁悦,秦础强,黄东生,等.原位自体骨与同种异体骨混合移植在腰椎后外侧融合术中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23(5):524-526. [26]敖俊,辛志军,陈方,等.两种植骨法对胸腰椎爆裂骨折复位后骨缺损空腔残存率及压缩刚度的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(8):974-979. [27]曾忠友,张建乔,金才益,等.经伤椎置钉椎弓根螺钉系统固定治疗胸腰椎骨折2年以上随访结果[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(2): 128-132. [28]赵镒汶,徐晓峰,曹兴兵,等.26例胸腰段压缩骨折后路短节段内固定术后矫正丢失的观察与分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(8):828-831. [29]印飞,张绍东,吴小涛,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉复位固定伤椎内植骨治疗Denis B型胸腰椎骨折的影像学观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(4):341-346. [30]贺聚良,詹新立,肖增明.不同植骨材料及方法对腰椎滑脱融合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(16): 3153-3156. [31]左健,康健敏,潘乐.同种异体骨移植用于骨缺损修复的应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3395-3398. [32]Takshashi H,Suguro T,Okazima Y,et al.Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1996;21(2):218-224. [33]Lorenzo J,Choi Y,Horowitz M,et al. Osteoimmunology: Interactions of the Immune and Skeletal Systems.Academic Press,2010:1-5. [34]刘建泉,于远洋,孔祥录,等.经椎弓根椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折的影像学观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,3(1):45-48. [35]Stevenson S,Li XQ,Davy DT,et al.Critical biological determinants of incorporation of non-vascularized cortical bone grafts:quantiflcation of a complex process and structure.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1997;79(1):1-16. [36]Vander Grriend RA.the effect of internal fixation on the healing of large allografts.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(5): 657-663. [37]Lin KY,Bartlett SP,Yaremchuk MJ,et al.The effect of rigrid fixation on the survival of onlay bone grafts:an experimental studay.Plast Peconstr Surg.1990;86(3):449-456. |
| [1] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [2] | Zou Shouping, Lu Daoyun, Ye Li. Minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw technique for thoracolumbar fractures: biomechanical changes of the spine during 6-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3865-3869. |
| [3] | Wang Ziao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen . Short-segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: method modification and strategies to reduce failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3902-3907. |
| [4] | Liu Gang, Zhang Baolu, Shi Jie, Bao Dingsu, Zeng Shengqiang, Deng Kai, Liu Yang, Wang Guoyou, Fu Shijie. Difference between proximal humeral locking plate and cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Mutch type II fracture of greater tuberosity of humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2863-2868. |
| [5] | Han Shichong, Li Chang, Xing Haiyang, Ge Wenlong, Wang Gang . Finite element analysis of two internal fixation methods for treating extra-articular proximal tibial fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2329-2333. |
| [6] | Zhao Binbin, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu, Li Yongqi, Wang Ning. Comparison of the osteogenic effect of three different bone graft materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1507-1510. |
| [7] | Jing Wanli, Zhang Tao, Teng Donghui, Shi Tao, Zhou Qiang. Poor outcomes of bone filling mesh container vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with vertebral body wall incompetence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1522-1527. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhiwei, Li Li, Huang Ziyu, Wu Duoyi, Gan Farong, Ye Baofei, Zhang Yan, Zhang Taibiao, Hu Wanjun. Percutaneous vertebroplasty through unilateral and bilateral pedicle approaches and unilateral pedicle extrapedicle approach for the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures: bone cement perfusion volume and cement leakage rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1353-1358. |
| [9] | Liu Yan, Ge Hongqing, Guan Hua, Chen Wenzhi. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods for poor medial column support proximal humeral fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1384-1389. |
| [10] | Wang Liang, Huang Zhaozhao, Yu Jiaona, Gu Weidong, Wang Ren, Qian Zhiyi. Biomechanical characteristics of bridge-link type combined internal fixation system with mixed-rod versus double-rod in the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 888-892. |
| [11] | Li Kaiming, Wang Shangquan, Li Linghui, Zhu Liguo, Zhang Qing, Xie Rui. Bone filling bag vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fractures: a meta-analysis of improving Cobb angle and reducing bone cement leakage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 650-656. |
| [12] | Mo Fan, Hua Qikai, Zhao Jinmin, Sha Ke, Xie Qi, Zhang Jin, Yang Yuan, Huang Weifeng, Wang Hao, Huang Hao, Chen Yinghua. Efficacy of free fibula transplantation combined with platelet rich plasma in the treatment of early necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5675-5681. |
| [13] | Weng Nengyuan, Zhang Tao, Li Kainan, Lan Hai, Zhang Jinli, Fu Xuefei, Liu Qixin, Lin Qingyun. A meta-analysis of efficacy and complications of 3D printing-assisted surgery for Schatzker IV-VI tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4889-4897. |
| [14] | Tu Dongpeng, Yu Yikang, Liu Zheng, Fan Xin, Zhang Wenkai, Xu Chao. Meta-analysis of locking plate combined with fibular allograft and locking plate alone in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4389-4397. |
| [15] | Huang Zhaoguo, Zhang Caiyi, Zhang Qing, Wang Sheng, Wang Shaogang, Li Jun, Tao Zhongliang, Zuo Caihong. Curative efficacy of proximal femoral nail antirotation versus intertrochanteric antegrade nail for treating intertrochanteric fracture in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3310-3314. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||